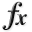 N-D Test Functions H¶
N-D Test Functions H¶Hansen test objective function.
This class defines the Hansen global optimization problem. This is a multimodal minimization problem defined as follows:
![f_{\text{Hansen}}(\mathbf{x}) = \left[ \sum_{i=0}^4(i+1)\cos(ix_1+i+1)\right ] \left[\sum_{j=0}^4(j+1)\cos[(j+2)x_2+j+1])\right ]](_images/math/53a08f06c4534d7300f28dc525ba491d11f90ec3.png)
Here, 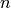 represents the number of dimensions and
represents the number of dimensions and ![x_i \in [-10, 10]](_images/math/d511ca3206c16bae3e3af3c02835f3fe9fb07286.png) for
for 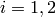 .
.
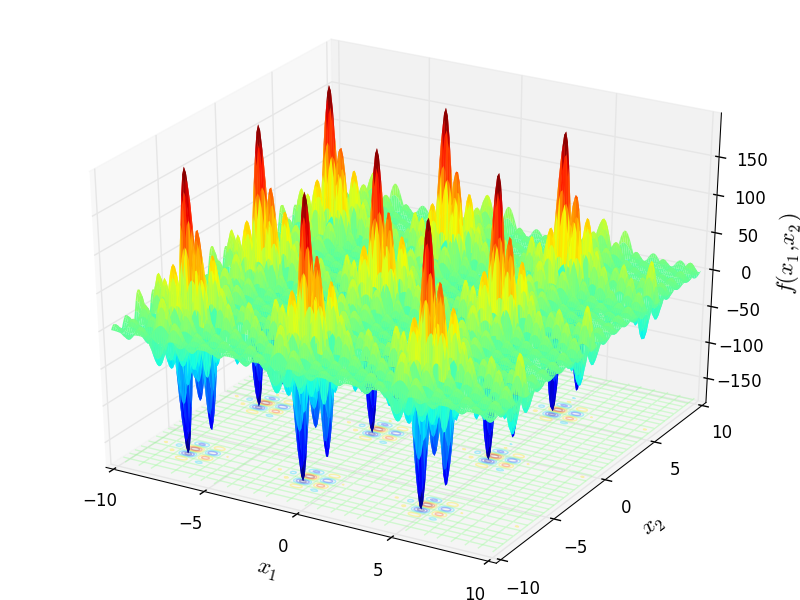
Two-dimensional Hansen function
Global optimum:  for
for ![\mathbf{x} = [-7.58989583, -7.70831466]](_images/math/44c64a3606016f87e619a914e92445fddc4041ae.png) .
.
Hartmann3 test objective function.
This class defines the Hartmann3 global optimization problem. This is a multimodal minimization problem defined as follows:
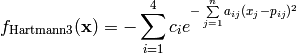
Where, in this exercise:
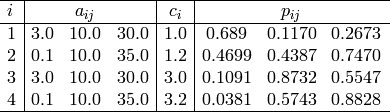
Here, 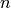 represents the number of dimensions and
represents the number of dimensions and ![x_i \in [0, 1]](_images/math/e365bfdf2ca5275ec86c322fa2fe576a37b0efd7.png) for
for 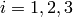 .
.
Global optimum: 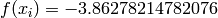 for
for ![\mathbf{x} = [0.1, 0.55592003, 0.85218259]](_images/math/9022e79bd9b50876858e33cdebc71ef1b535dfda.png)
Hartmann6 test objective function.
This class defines the Hartmann6 global optimization problem. This is a multimodal minimization problem defined as follows:

Where, in this exercise:

Here, 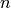 represents the number of dimensions and
represents the number of dimensions and ![x_i \in [0, 1]](_images/math/e365bfdf2ca5275ec86c322fa2fe576a37b0efd7.png) for
for 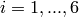 .
.
Global optimum: 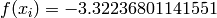 for
for ![\mathbf{x} = [0.20168952, 0.15001069, 0.47687398, 0.27533243, 0.31165162, 0.65730054]](_images/math/019cc50160e9303e9136dd974ab92417dbb7216b.png)
HelicalValley test objective function.
This class defines the HelicalValley global optimization problem. This is a multimodal minimization problem defined as follows:
![f_{\text{HelicalValley}}(\mathbf{x}) = 100{[z-10\Psi(x_1,x_2)]^2+(\sqrt{x_1^2+x_2^2}-1)^2}+x_3^2](_images/math/5473c2351accc35805871ed91cca347c88a06f41.png)
Where, in this exercise:
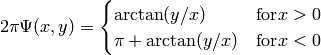
Here, 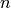 represents the number of dimensions and
represents the number of dimensions and ![x_i \in [-\infty, \infty]](_images/math/89b78d1679eba63ccfe13d1418785847a9c86640.png) for
for 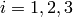 .
.
Global optimum: 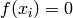 for
for ![\mathbf{x} = [1, 0, 0]](_images/math/72557da9e0762f7634d8202b5c73c12e47e1610b.png)
HimmelBlau test objective function.
This class defines the HimmelBlau global optimization problem. This is a multimodal minimization problem defined as follows:
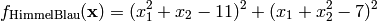
Here, 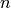 represents the number of dimensions and
represents the number of dimensions and ![x_i \in [-6, 6]](_images/math/4ac04453fa34db4ac100caa22aced4c378598e65.png) for
for 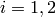 .
.
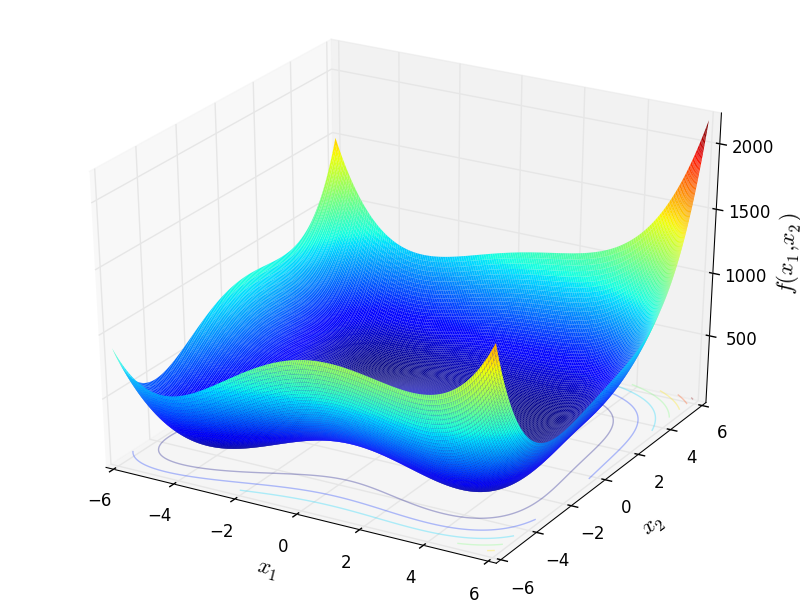
Two-dimensional HimmelBlau function
Global optimum: 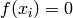 for
for ![\mathbf{x} = [0, 0]](_images/math/ae446016118c18b04012af8feda9cc5e2e1808a6.png)
HolderTable test objective function.
This class defines the HolderTable global optimization problem. This is a multimodal minimization problem defined as follows:
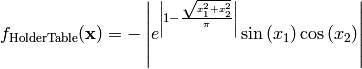
Here, 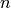 represents the number of dimensions and
represents the number of dimensions and ![x_i \in [-10, 10]](_images/math/d511ca3206c16bae3e3af3c02835f3fe9fb07286.png) for
for 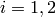 .
.
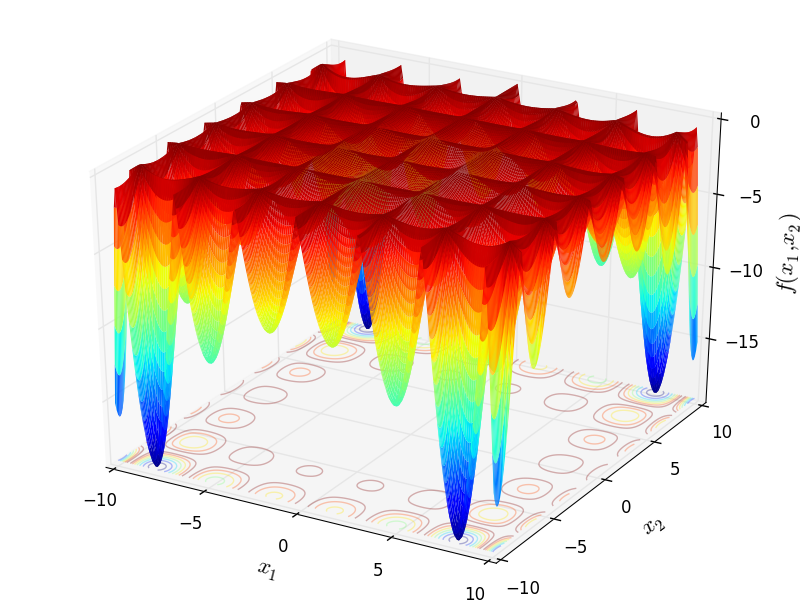
Two-dimensional HolderTable function
Global optimum:  for
for 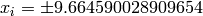 for
for 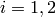
Holzman test objective function.
This class defines the Holzman global optimization problem. This is a multimodal minimization problem defined as follows:
![f_{\text{Holzman}}(\mathbf{x}) = \sum_{i=0}^{99} \left [ e^{\frac{1}{x_1} (u_i-x_2)^{x_3}} -0.1(i+1) \right ]](_images/math/d416f9cfe90c36b25c99923f3453b338e40ee90c.png)
Where, in this exercise:
![u_i = 25 + (-50 \log{[0.01(i+1)]})^{2/3}](_images/math/a77ce0eb3b606fc59b53f7995f5ebf997c339ed3.png)
Here, 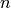 represents the number of dimensions and
represents the number of dimensions and ![x_1 \in [0, 100], x_2 \in [0, 25.6], x_3 \in [0, 5]](_images/math/a845c15aeca0c97047d6279954d0dc42af904692.png) .
.
Global optimum: 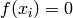 for
for ![\mathbf{x} = [50, 25, 1.5]](_images/math/213fecbadfdaff832486b641e83587ac11937340.png)
Hosaki test objective function.
This class defines the Hosaki global optimization problem. This is a multimodal minimization problem defined as follows:
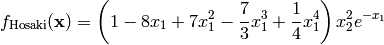
Here, 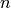 represents the number of dimensions and
represents the number of dimensions and ![x_i \in [0, 10]](_images/math/04492218e68759ff19d07231a62fe3a092015dfc.png) for
for 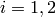 .
.
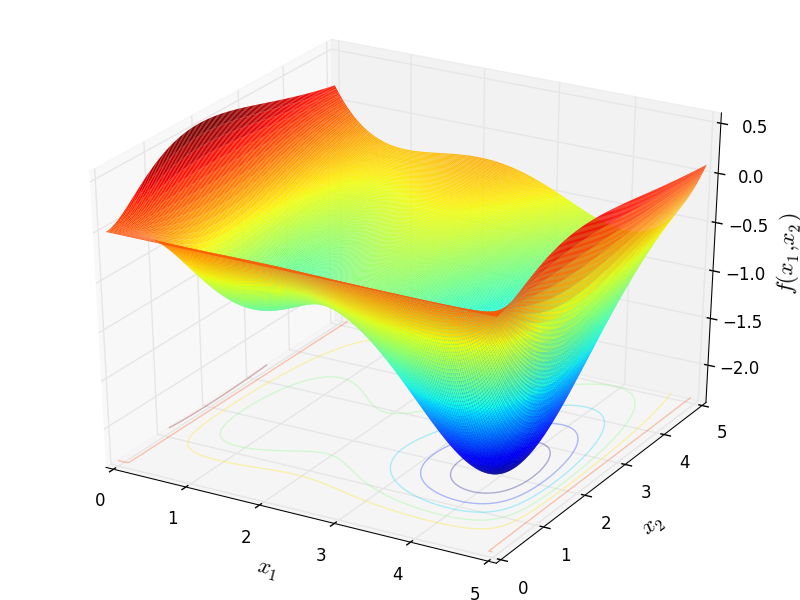
Two-dimensional Hosaki function
Global optimum:  for
for ![\mathbf{x} = [4, 2]](_images/math/778c4e85066794f513c083557f5efd8b0b0a0112.png) .
.